Welcome to the world of Price Action Trading for Dummies. Let’s unravel the basics of this trading approach that simplifies complex concepts.
Also Read: 3 Most Accurate Candlestick Patterns every Trader should know
Price Action Trading, or PAT, offers a straightforward way to navigate the intricate world of financial markets. Instead of relying on complicated indicators like MACD or Stochastics, we focus on pure price movements. It’s like learning to read the language of markets through Japanese candlesticks, trend lines, and essential support and resistance levels.
Who Benefits from Price Action Trading?
Price Action Trading is especially helpful for beginners and those who find comfort in clear chart patterns for forecasting future price moves. But it’s not limited to them. Seasoned traders, arbitrageurs, speculators, and even high-frequency trading firms incorporate Price Action principles into their strategies.
Where Can You Apply Price Action Trading?
Price Action Trading is versatile and fits various securities. You can apply it to Forex, Derivatives, Equities, Commodities, Bonds, and more.
How Does Price Action Trading Work?
Price Action Trading is all about recognizing visible patterns in price charts and making informed decisions. Experienced Price Action traders pay close attention to entry/exit levels, stop-loss points, and targets based on their observations. They understand that a single strategy won’t work for every stock. The Price Action Trading process typically involves two steps:
- Identify the Scenario: Examine the stock’s price movement to determine whether it’s in a bear or bull phase, its channel range, and potential breakouts.
- Spot Trading Opportunities: After identifying the scenario, traders pinpoint opportunities based on their analysis. Selecting the right opportunity is subjective and varies from trader to trader. For example, when a stock reaches a high and later retreats, one trader may anticipate a double top, while another may predict a mean reversion. It all depends on individual judgment.
Examples of Price Action Trading
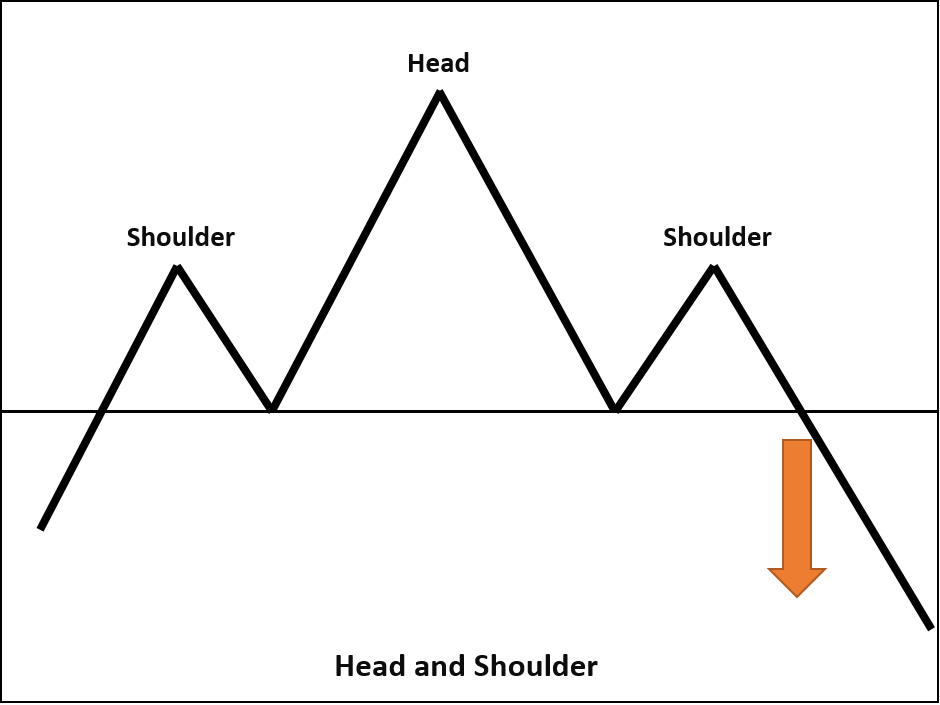
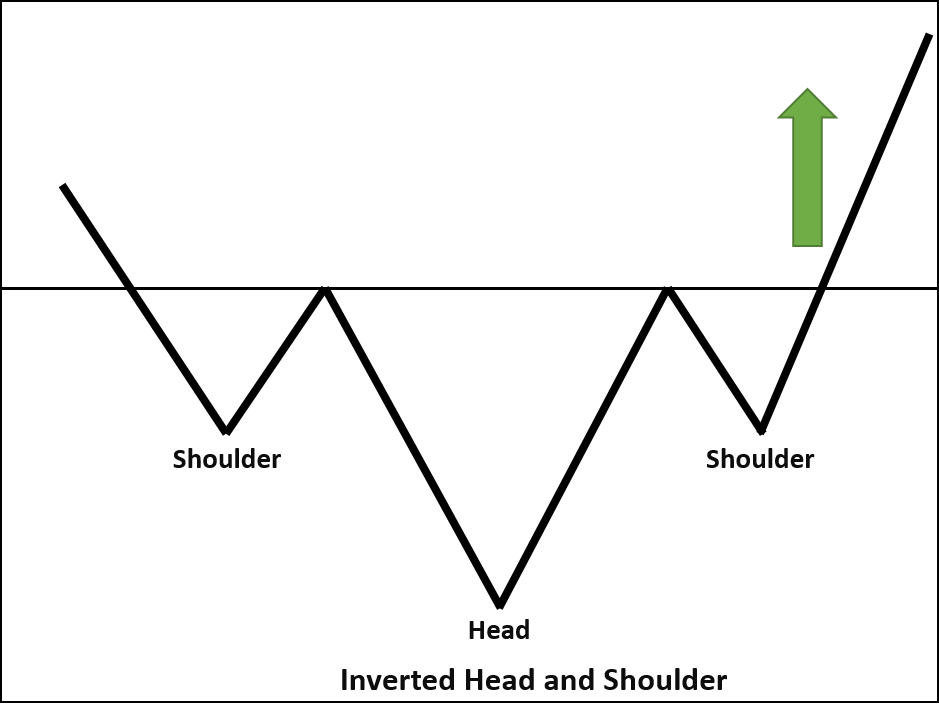
Head and Shoulders
The Head and Shoulders pattern features two nearly identical peaks with a higher peak in between. The trough between the shoulders is called the “neckline.” If the price breaks the neckline after reaching the second shoulder, it signals a bearish reversal in an ongoing uptrend. The inverse pattern is known as “Inverted Head and Shoulders,” indicating a bullish reversal during a downtrend.
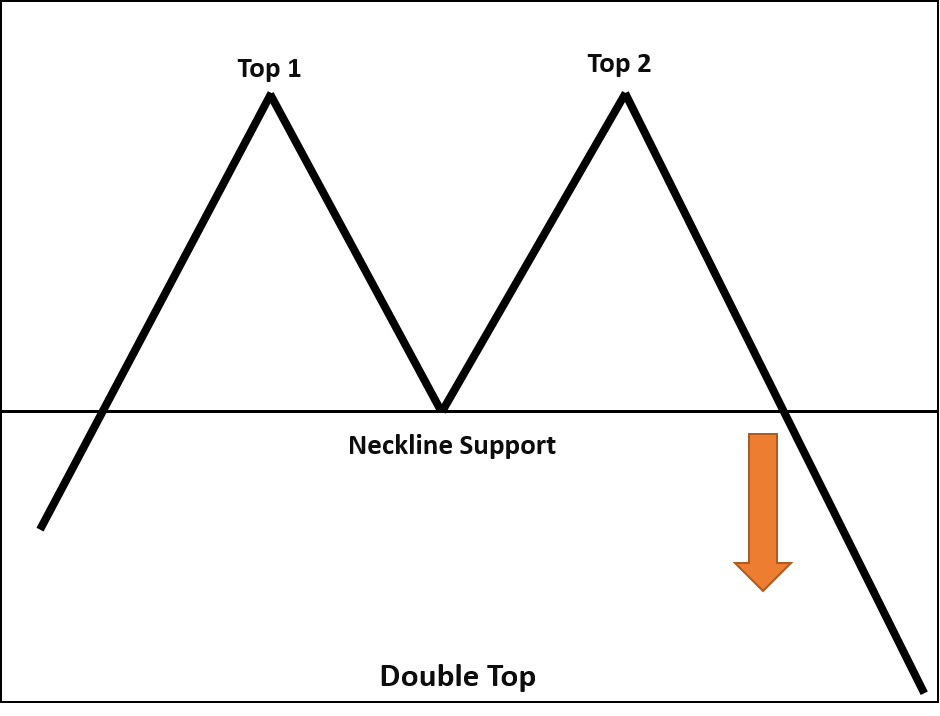
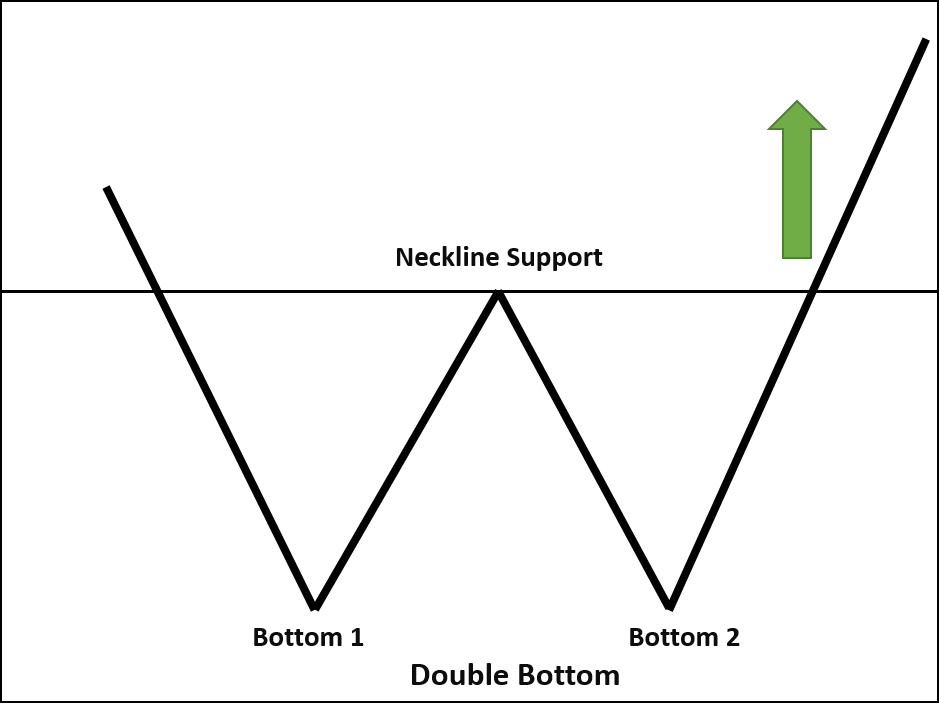
Double Top and Double Bottom
The Double Top pattern, similar to Head and Shoulders, lacks the “Head.” It consists of two nearly identical peaks side by side. If the price breaks the previous swing low between the two peaks after reaching the second high, it signals a bearish reversal. The Double Bottom pattern involves two nearly identical troughs. A breakout from the previous swing high indicates a bullish reversal.
Bullish and Bearish Engulfing Candlestick Pattern
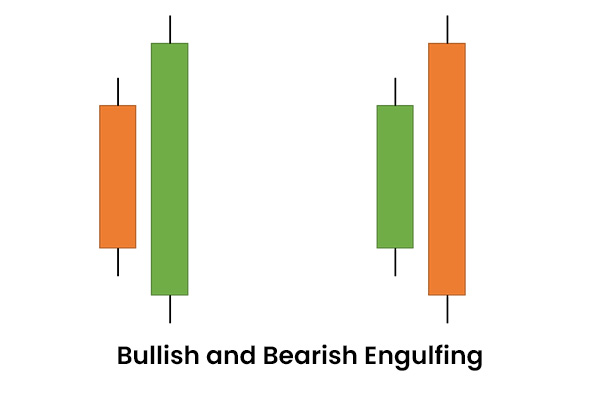
The Bullish Engulfing pattern involves a short candle followed by a tall one that completely engulfs the short one. A Bearish Engulfing pattern is the opposite, with a green-bodied candlestick followed by a longer red-bodied candlestick. These patterns offer powerful signals and are widely favored by traders for decision-making.
Also Read: Understanding Candlestick Patterns in Stock Analysis
Price Action Trading Jargons
Price Action Trading relies on comprehensive technical analysis jargon, including charts, swings (high and low), consolidation and resistance levels, price bands, trend lines, breakouts, candlesticks, channels, volatility, and more. The approach leaves room for traders to interpret behavioral and psychological aspects. For instance, while watching a stock move from 580 to 600, one trader might anticipate further gains, while another might expect a reversal at 600.
Also Read: 123 Trading Strategy: Profitable Chart Patterns
In conclusion, Price Action Trading offers a systematic approach to trading. By considering historical price movements and utilizing technical analysis tools, traders can make well-informed decisions based on their judgment.





7 Comments