In the realms of stock trading and Futures & Options (F&O), Open Interest (or OI)stands as a vital parameter that merits attention. It’s widely acknowledged that many institutional traders base their trades predominantly on it, often setting aside other indicators or chart patterns.
Let’s explore the importance of Open Interest in financial markets.
Overview of Open Interest
According to Investopedia, Open Interest represents the total number of outstanding derivative contracts, such as options or futures, that remain unsettled for an asset.
Detailed calculations of OI are available, with comprehensive insights offered in this resource.
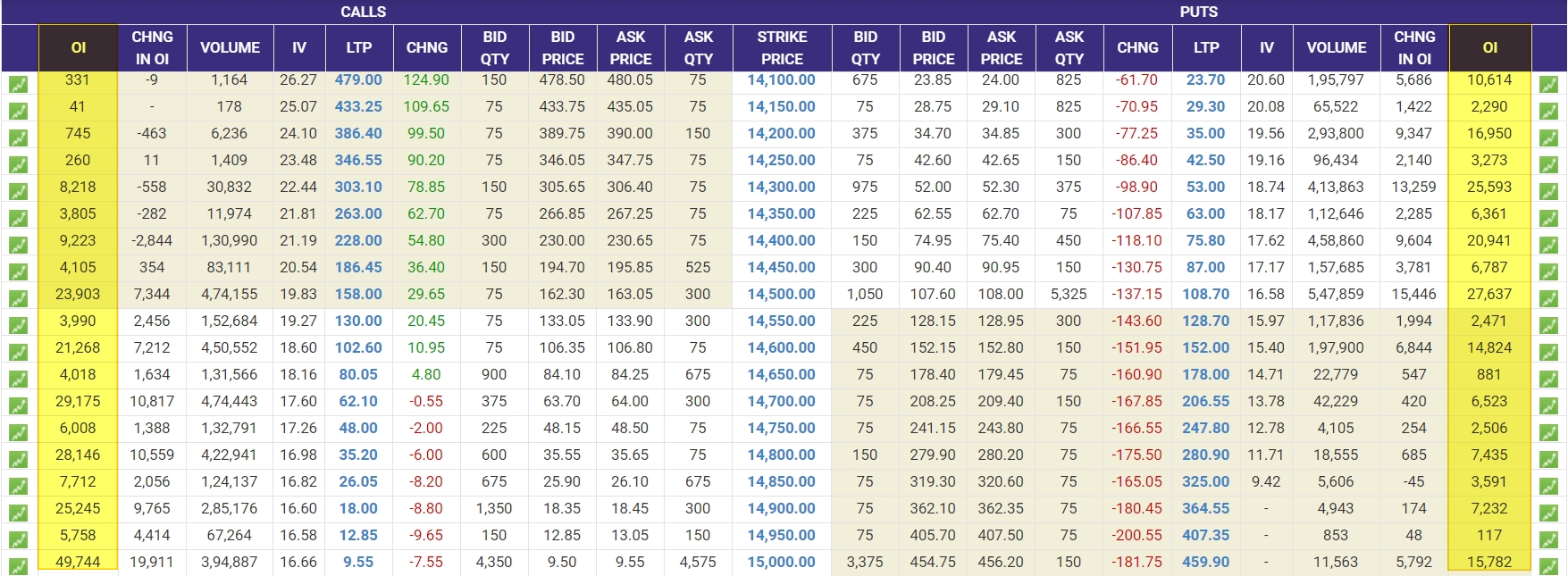
Every strike in an option chain possesses an individual Open Interest value. OI For any given strike increases when trades occur on that strike.
For instance, Open Interest for Nifty 14000 CE rises by one if a trader buys one lot of this contract while another sells one lot. Conversely, it decreases by one when these positions are squared off.
Significance of Open Interest
Three critical aspects underscore the importance of Open Interest as a definitive market indicator:
- Option contract selling demands significant capital, typically indicating that sellers are individuals or entities with large funds, accepting the risk of unlimited loss.
- Conversely, buying an options contract requires less capital and entails limited risk, making it a prevalent choice among retail traders.
- Large capital holders, such as institutional traders, often have the right market predictions, thanks to their extensive resources.
When a particular strike exhibits high Open Interest, it usually indicates that institutional traders are selling, while retail traders are buying. This strike then becomes a pivotal point of resistance or support, as institutional traders aim to avoid losses if the underlying price surpasses that strike.
Related Reading: Elevate Your Trades: The Power of Technical Analysis
Utilizing OI in Trading Strategies
To leverage Open Interest in trading, one should:
- Identify the Call strike with the highest OI for potential Resistance:
- Consider selling that strike, or
- Sell a futures contract when the underlying price approaches that strike.
- Pinpoint the Put strike with the highest OI for Support:
- Contemplate selling that strike, or
- Buy a futures contract as the underlying price nears that strike.
- Consider a short strangle by selling both the highest OI Call and Put strikes for a higher probability of success.
Implementing these strategies can significantly boost the success rate in trading.
Accessing Open Interest Data
Open Interest data for futures and options is readily accessible:
- Directly from exchange websites, like the NSE Nifty option chain available at this link.
- Through a broker’s dashboard, where OI data is often displayed for each symbol in a watchlist.
- Using external data feeds like Truedata or GDFL, allowing historical OI data import into tools like Amibroker.
- With excel-based tools that facilitate fetching OI data from exchange websites, as detailed here.
Conclusion
The role of OI in predicting market movements is undeniable. When coupled with other technical analysis indicators, Open Interest can help develop highly accurate trading systems.
For any queries or further information, feel free to engage in the comments section.



One Comment