Introduction to Options in Trading: If you’re new to trading, understanding options in derivatives trading is crucial. These contracts grant the right to buy or sell underlying assets under specific conditions.
Options come with a pre-determined price and expiry date, giving traders flexibility and control.
In this article, we’ll delve into the two main types of options: call options and put options, providing a comprehensive overview.
Also Read: Black Scholes Options Premium Calculator Spreadsheet
Exploring Call Options
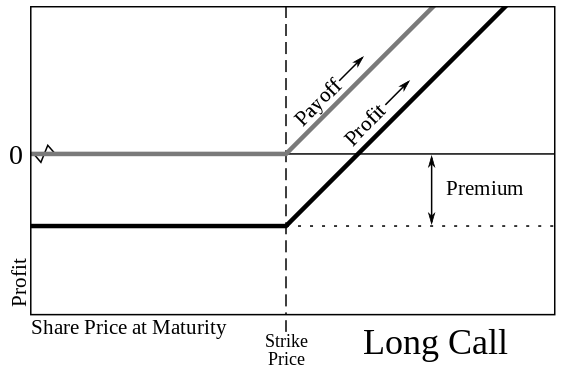
A call option is a contract allowing the buyer to purchase an asset within a set timeframe at a specified price.
To acquire a call option, the buyer pays an option premium, which is the asset’s current price. Once purchased, it’s the owner’s choice to exercise the option as they see fit.
You can let an unprofitable call option expire. Conversely, the seller must sell the asset if the buyer chooses. The beauty of a call option lies in its limited losses and potentially unlimited profits.
Call Option in Practice
For a clearer understanding, let’s examine a call option example. Imagine an investor purchases a call option for XYZ company’s stocks at a strike price of $2.
Should the stock price climb above $2, say to $2.50, the investor can still buy at $2. A call option is ideal when anticipating a stock price increase, promising future gains.
Types of Call Options
Call options are categorized as:
- In the Money: When the current security price exceeds the strike price.
- Out of the Money: When the current security price is below the strike price.
- At the Money: When the current security price equals the strike price.
Understanding Put Options
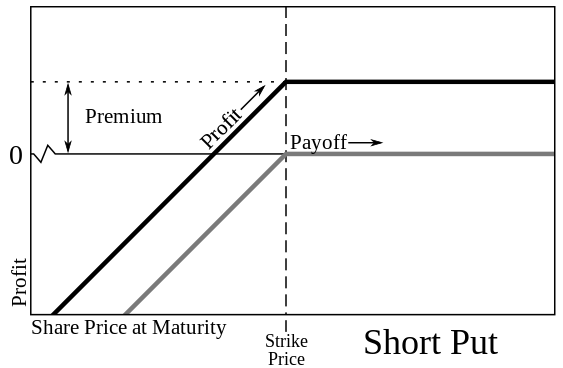
A put option empowers the holder to sell an asset within a specific period at pre-determined prices, securing a minimum sale price.
Like call options, put options don’t obligate the investor to exercise their rights. If the current price exceeds the strike price, selling at the market price is possible.
Put Option Example
Let’s demystify put options with an example. Suppose an investor buys a put option for ABC company, allowing asset sales at $2 before expiry.
If the share price dips below $2, say to $1.75, the investor can still sell at $2. This flexibility minimizes risk when prices fall.
Types of Put Options
Put options also come in two types:
- In the Money: When the current price is less than the strike price.
- Out of the Money: When the current market price is above the strike price.
- At the Money: When the market price equals the strike price.
Also Read: Delta Neutral Option Strategies
Conclusion: Making Smart Choices in Options Trading
In summary, traders opt for call options expecting a price rise, while put options are chosen when a price drop is anticipated.
Options trading is highly active globally, often surpassing equity trading volumes.
Trading might seem daunting, but mastering the basics, like understanding different options, paves the way for smart investing.




One Comment